Have you ever thought about what happens when the lights go out and all your favorite gadgets stop working? It’s like the whole world pauses! But don’t worry, there’s something cool called a generator that can bring everything back to life, like magic!✨
But here’s the thing: not all generators are the same. You need the right size to keep everything working just the way you want.
To calculate generator size, add up the total wattage of all the appliances you plan to power. Then, select a generator with a capacity 20–25% higher than this total. Accurately calculating generator size helps maintain consistent power, protect your equipment, and extend the lifespan of your generator.
So today, we’re going to figure out how to choose the perfect generator size, step by step. It’s gonna be fun and easy – pinky promise!🤞

Why Does Generator Size Matter?
Alright, imagine this: You’re trying to water your garden with a straw instead of a hose. 🌻🌱 Would that work? Nope! The straw is way too small. The same thing happens with a generator. If it’s too small, it won’t be able to power all your stuff. But if it’s too big, it’s like using a fire hose to water one flower – way too much! So, we need to find a generator that’s just right! 🎯
Understanding Power Needs
To understand the power needs, you have to learn about wattage and voltage. Wattage measures the electrical power of devices. Multiplying volts by amps yields wattage. Let’s get a bit of detail on them.
What’s a Watt?💡
Okay, here’s a new word for you: watt. A watt is a way to measure power. Think of it like how we measure how fast a car is going in miles per hour or how much a bag of candy weighs in pounds. The more watts something needs, the more power it needs to work.
Definition: A watt (W) is a unit of power in the International System of Units (SI).
It measures the rate at which energy is used or generated. One watt is equivalent to one joule of energy per second. In practical terms, it indicates how much energy an electrical device consumes or produces per second.
For example, a 60-watt light bulb uses 60 joules of energy every second it is on. Similarly, if a power plant produces 1000 watts, it is generating 1000 joules of energy per second.
Watts vs. Volts: The Power Duo!⚡️
Now, there’s another word: volts. Volts are like the pressure that pushes the power to your gadgets. Imagine you’re pushing a toy car across the floor. The harder you push, the faster it goes. Volts are like the push, and watts are like how fast the car goes. Together, they make your devices work their best!
Making a List of Appliances
Your Favorite Gadgets and Gizmos 🎮
Time to make a list of all the cool stuff you want to keep running when the power goes out. Do you have a game console, a TV, or maybe a lamp for reading your favorite book? Write them all down! 📜
Big Power Users: AC, Fridge, and More 🧊
Now, let’s think about the big things in your house. Things like the air conditioner, the fridge, and maybe even the washing machine. These guys need more power to keep running, so they’re super important when choosing your generator size.

Adding Up the Power Needs
The Math Magic of Addition! 🧮
Now comes the fun part – adding up all those watts! Each gadget or appliance you listed has a certain number of watts it requires. Just like how you add up the points in a game, you add these numbers together to find out how much total power you require.
Here’s a wattage chart for essential home gadgets you might want to run with a generator during a power outage. The actual wattage may vary depending on the model and usage, but this should give you a general idea.
| Device | Average Running Wattage (W) | Starting Wattage (W) |
|---|---|---|
| Refrigerator/Freezer | 600 – 800 | 1200 – 1600 |
| Microwave Oven | 800 – 1200 | 800 – 1200 |
| Sump Pump (1/2 HP) | 1000 – 1500 | 2000 – 3000 |
| Electric Water Heater | 3000 – 4500 | 3000 – 4500 |
| Air Conditioner (Window) | 600 – 1500 | 1200 – 4500 |
| Television (LED/LCD) | 100 – 300 | 100 – 300 |
| Laptop Charger | 50 – 100 | 50 – 100 |
| Wi-Fi Router/Modem | 10 – 50 | 10 – 50 |
| Lighting (per bulb) | 5 – 60 (LED/CFL) | 5 – 60 |
| Ceiling Fan | 60 – 100 | 150 – 300 |
| Washing Machine | 500 – 1200 | 1200 – 3000 |
| Coffee Maker | 800 – 1200 | 800 – 1200 |
| Toaster | 800 – 1500 | 800 – 1500 |
| Space Heater | 750 – 1500 | 750 – 1500 |
| Electric Stove (1 burner) | 1000 – 1500 | 1000 – 1500 |
Notes:
- Running Wattage: The power required to keep the device running.
- Starting Wattage: The power required to start the device, typically higher due to the initial surge needed to get motors or compressors running.
Sum up the total starting watts and running watts. This helps you choose the right generator size. Ensure your generator can handle the highest load. This will prevent overloading and keep your appliances safe.
Understanding Starting vs. Running Watts🏃♂️
In the above chart, we see that most of the appliances need more power to start than run. What’s the secret behind it? Let’s explore: some things need a big burst of power to get started, like when you need a lot of energy to start running but not as much to keep going. These are called starting watts.
After they’re up and running, they use less power, which is called running watts.
It’s important to know both to pick the right generator!
Starting watts (also known as surge watts) refer to the higher amount of power needed to start an electrical device, particularly those with motors or compressors. When a device first turns on, it often requires a brief surge of energy to get up and running.
Running watts (also known as rated watts) refer to the continuous power a device needs to operate once it is already running.
Example:
Consider a refrigerator:
- Starting Watts: A refrigerator might require 1200 watts to start because the compressor needs extra power to begin cooling.
- Running Watts: Once the refrigerator is running, it only needs about 600 watts to keep operating.
So, when using a generator, you need to account for both the higher starting wattage and the lower running wattage to ensure it can handle the initial surge as well as the continuous load.
Choosing a Generator Type
Now, let’s talk about the types of generators. Typically, there are two types of generators: portable and standby.
Portable generators 🚗 are easy to move, like a toy you can take to a friend’s house. These are great for camping or small needs. Portable generators can power some home appliances too. Always check the power rating before using one.
Standby generators 🏠 that stay at home and are always ready to jump in when the lights go out. These generators can power an entire house. They use natural gas or propane. Standby generators need regular maintenance.
Now, you have to decide which one sounds better to you? 😊

Safety First: Don’t Forget the Surge Watts!
What Are Surge Watts? 🚨
Remember those starting watts we talked about? Sometimes, appliances need even more power when something unexpected happens, like a surge. Surge watts are like extra power reserves your generator needs to handle surprises.
Why They’re Super Important! ⚠️
Imagine you’re on a rollercoaster—the ride suddenly speeds up! That’s like a power surge, and if your generator can’t handle it, you could lose power when you need it most. So, make sure your generator has enough surge watts to keep everything running smoothly.
Calculating The Surge Power⚡
When choosing a generator, it’s generally recommended to account for a surge power of 20–30% above the total running wattage of the devices you plan to use. This safety margin ensures that the generator can handle the initial surge required by devices when they start up.
Example:
If the total running wattage of your essential devices is 3000 watts, you should add a surge power margin of 20-30%.
- 20% Surge Margin: 3000 x 1.2 = 3600 watts
- 30% Surge Margin: 3000 x 1.3 = 3900 watts
So, you would look for a generator with a capacity of at least 3600-3900 watts to safely handle the startup surges.
Factoring in Extra Power for Future Needs📝
Planning Ahead Like a Power Pro. Sometimes, we get new toys or gadgets. To make sure your generator can handle anything new, it’s smart to add a little extra power to your total wattage.
To avoid power problems later, you can list down the current appliances. Estimate their power needs. Add the possible future devices.
Think of it as being prepared for the next big adventure! 🚀
Fuel Types and How They Affect Generator Size⛽️
Gasoline, Propane, Diesel—Oh My! Generators can run on different types of fuel. Some like gasoline, which is easy to find, but it can run out fast. Others prefer propane, which burns clean but needs a big tank. And then there’s diesel, which is super powerful but can be smelly.
The type of fuel your generator uses can change how big it needs to be.
Don’t Forget About Weather Conditions🌡️
Generators work differently in different weather. If you live somewhere hot, your generator might need to work harder, just like how we sweat more in the heat.
If it’s super cold, your generator might need a little extra help to start up. Keep the weather in mind when picking your generator size!
Checking the Manufacturer’s Guide📖
Why the Manual is Your Best Friend? Every generator comes with a manual, like a secret code book! This guide tells you everything you need to know about how your generator works and what it can handle. Don’t skip it—it’s your ticket to being a generator genius! 😎
Generator Calculations Formulas
Here are some basic formulas for calculating the generator size you need:
1. Total Running Watts Calculation:
Total Running Watts = ∑Running Watts of All Devices
Add up the running watts of all the devices you plan to power.
2. Starting Watts Calculation:
Total Starting Watts = Highest Starting Watts + Total Running Watts
Use the device with the highest starting watts, then add it to the total running watts.
3. Generator Size Calculation:
Recommended Generator Size (Watts) = Total Running Watts × 1.2 to 1.3
Multiply the total running watts by 1.2 to 1.3 to account for surge power.
These formulas will help ensure that your generator can handle both the continuous and startup power needs of your home.
Finalizing Your Generator Size🔍
Let’s Add It All Up! Alright, now that you’ve got your list of gadgets, know your starting and running watts, and have factored in future needs and weather, it’s time to make your choice. Add it all up, double-check your numbers, and you’ll know exactly what size generator you need!🎉
Don’t Get Caught Without Enough Power!😱
One of the biggest mistakes is not choosing a generator with enough power. Remember, it’s better to have a little too much than not enough. And don’t forget those surge watts—they’re lifesavers!
What size generator do I need for my house chart?
Here’s a chart to help you determine the size of the generator you might need for your house. The wattages listed are approximate and can vary depending on the specific devices you use.
| Home Size/Needs | Typical Devices | Estimated Total Running Watts | Suggested Generator Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small Home (1-2 rooms) | Lights, refrigerator, TV, laptop, fan, microwave | 2000 – 4000 watts | 4000 – 5000 watts |
| Medium Home (3-4 rooms) | Small appliances, lights, refrigerator, TV, fan, sump pump, microwave | 4000 – 7000 watts | 7000 – 9000 watts |
| Large Home (5+ rooms) | Large appliances, AC units, lights, refrigerator, well pump, heater | 7000 – 10,000 watts | 10,000 – 12,000 watts |
| Whole-House Backup | All major appliances, heating/cooling systems, lights, electronics | 10,000 – 15,000+ watts | 15,000 – 20,000 watts |
Always calculate the total wattage of the devices you need to power and add 20–30% for surge capacity to select the appropriate generator size.
Generator Sizing Calculator Excel
Find below a step-by-step guide to help you build a simple generator sizing calculator. You can create this calculator by using basic tools like Excel or Google Sheets. Let’s started.
Step 1: List Devices and Their Wattages
Create columns for:
- Device Name
- Running Watts
- Starting Watts (if applicable)
Step 2: Input Device Data
Manually enter the running and starting watts for each device you want to power with the generator.
Step 3: Calculate Total Running Watts
Sum the running watts of all devices using the following formula.
Total Running Watts = ∑Running Watts of All Devices
Step 4: Calculate Surge Requirement
Find the device with the highest starting watts. Add this to the total running watts to calculate the total starting wattage.
Total Starting Watts = Highest Starting Watts + Total Running Watts
Step 5: Add a Safety Margin
Multiply the total running watts by 1.2 to 1.3 to account for surge power.
Step 6: Display the Recommended Generator Size
Finally, display the recommended generator size in watts based on the calculations.
Example Using Excel/Google Sheets
- Column A: Device Name
- Column B: Running Watts
- Column C: Starting Watts (if any)
- Cell D1: Total Running Watts:
=SUM(B2:B10) - Cell D2: Highest Starting Watts:
=MAX(C2:C10) - Cell D3: Total Starting Watts:
=D1 + D2 - Cell D4: Recommended Generator Size:
=D1 * 1.2(or use 1.3 for a higher margin)
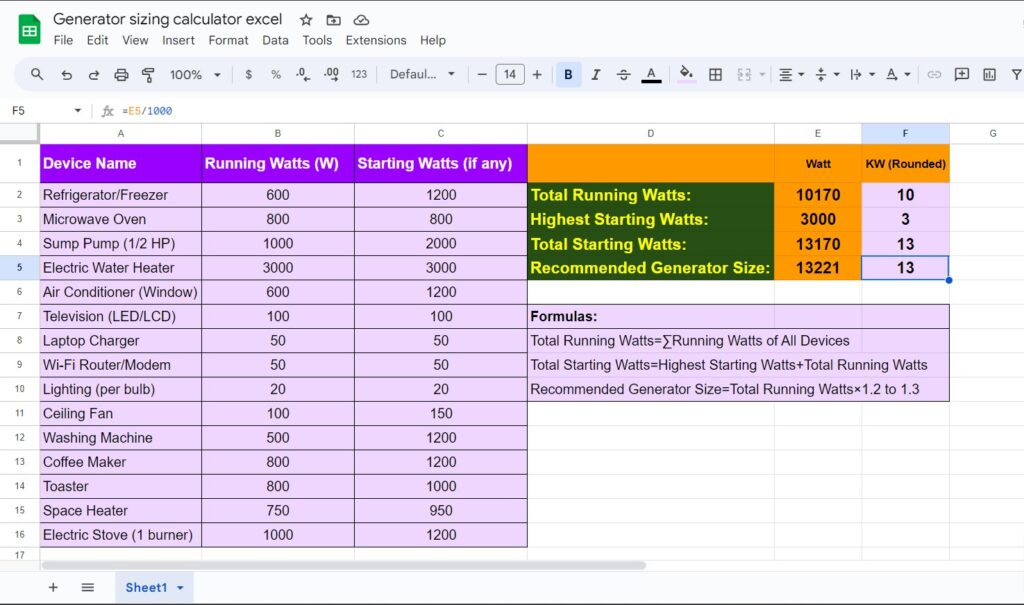
Step 7: Test and Adjust
Test the calculator with different devices to ensure accuracy. Adjust the safety margin or add more features as needed.
This simple calculator should help you determine the appropriate generator size for your home needs.
Safety And Installation Tips
Generators need proper ventilation to avoid dangerous fumes. Place the generator in an open area. Keep it away from windows and doors. Make sure exhaust fumes do not enter the house. This will help prevent carbon monoxide poisoning. Carbon monoxide is a silent killer. Always use a carbon monoxide detector for safety.
Hire a professional for generator installation. They ensure all connections are safe. Professionals follow local codes and regulations. Incorrect installation can be dangerous. It might void the warranty. Trained experts know the best practices. This guarantees safe and efficient operation.
Maintenance And Longevity
Regular servicing keeps your generator running smoothly. It helps prevent unexpected breakdowns. Check the oil levels frequently. Clean or replace the air filters as needed. Ensure the spark plugs are in good condition.
Inspect the fuel system for any leaks. Regularly test the battery and charging system. Keep the cooling system clean and free from debris.
Store the generator in a dry and cool place. Keep it away from direct sunlight. Use a cover to protect it from dust. Make sure the fuel tank is empty before long storage.
Disconnect the battery to avoid drainage. Clean the generator before storing it. Check for any signs of wear or damage.
FAQs: How Do I Calculate Generator Size?
How Do I Calculate How Big Of A Generator I Need?
Calculate the generator size by adding the wattage of all devices you plan to power. Include a 20% buffer.
What Is The Formula For Calculating A Generator?
The formula for calculating generator power is:
Power (kW) = Voltage (V) x Current (A) x Power Factor (PF) / 1000.
How Big Of A Generator Do I Need For A 2000 Sq Ft House?
A 2000 sq ft house typically needs a 15-20 kW generator. This size covers essential appliances and systems.
What factors determine generator size?
Generator size is determined by total wattage, type of appliances, and usage duration.
Why is surge wattage important?
Surge wattage accounts for the initial power surge when starting appliances, ensuring the generator can handle the load.
Do I need a special place for my generator?
Yes, generators should be kept in a well-ventilated area outside to avoid dangerous fumes. Never run them inside your house!
Is it okay to use a generator in bad weather?
Generators can be used in bad weather, but they should be protected from rain and snow. Always use them in a dry, safe place to avoid any issues.
How Many Watts Does Your Generator Need!
Conclusion
Now you know how to choose the perfect size to keep your house powered up, no matter what. Whether it’s for a cozy movie night during a storm or keeping your ice cream from melting in the fridge, you’re ready to pick the right generator with confidence.
Don’t forget to check your list and maybe even ask an expert for help. And remember, you’re a power-sizing pro now! 🎉
Recent Posts
Woodworking in 2025 is all about efficiency, precision, and smart technology. Whether you're a beginner or a seasoned craftsman, having the right tools can make all the difference. Here are the top 7...
Ever tried drilling into a piece of wood only to end up with a splintered mess or a wobbly hole? Yeah, it's more common than you think. Wood might seem like an easy material to work with, but...

